Security in Outsourced Databases
| Overview |
In the Outsourced Database Model (ODB), organizations outsource their data management needs to an external service provider. The service provider hosts client's databases and offers seamless mechanisms to create, store, update and access (query) their databases. This model introduces several research issues related to data security which we explore.
| System Model |
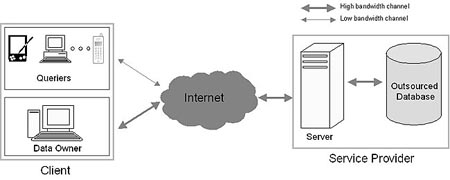
The Outsourced Database Model consists of 3 entities: (1) the data owner(s), (2) the database service provider (server) and (3) the client(s) (also referred to querier(s)). The data owner creates, modifies and deletes the contents of the database. The server hosts the owner's database, i.e., the owner outsources its database to the server. The clients issue queries about the database to the server.
Some of the parameters identifying a specific ODB include the number of owners and clients and the type of trust in the server. Is the server trusted with the data contents but not with integrity? Or do we not trust the database administrators and therefore need to employ encryption to provide data privacy?
| Objectives |
We wish to address various security issues that arise in the Outsourced Database Model. These range from providing data confidentiality, authenticity and integrity, to enabling an untrusted server to run queries over encrypted data. We also focus on the performance aspects of our solutions.
-
Authenticity and Integrity
Using signatures we provide mechanisms to allow the querier (client) to ensure that the records returned from the untrusted server originated from the data owner and have not been tampered with. We aim at minimizing the bandwidth and computation required to enable this verification. A new signature scheme, Condensed-RSA, is proposed and we compare its performance with an elliptic curve based signature scheme introduced by Boneh, et al. -
Data Privacy
If the database server is fully untrusted, the measures need to be taken such as to protect the owner's data privacy. The goal is to hide the data contents from the server, by employing data encryption, while still allowing the server to operate the database. In other words the challenge can be formulated as: how to allow the server to perform queries over encrypted data. -
Efficient Secure Storage Model in RDBMS
Several database vendors already offer integrated solutions that aim to provide data privacy within existing products. Treating security and privacy issues as an afterthought often results in inefficient implementations. Some notable RDBMS storage models (such as the N-ary Storage Model) suffer from this problem. We analyze issues in storage, looking at trade-offs between security and efficiency, and then propose a secure storage model, Partition Plaintext Ciphertext (PPC), which enables efficient cryptographic operations while maintaining a high level of security.
| People |
- Principal Invesitagors (UCI)
- Graduate Student Researchers (UCI)
- Bijit Hore
- Ravi Jammalamadaka
- Einar Mykletun
- Maithili Narasimha
- Yonghua Wu
| Publications |
- Privacy and Authenticity/Integrity
-
Aggregation Queries in the
Database-As-a-Service Model
Data and Application Security (DBSEC 2006), July 2006 -
Authentication of Outsourced Databases using Signature Aggregation and Chaining
International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications (DASFAA 2006), Apr 2006 PDF
-
DSAC: Integrity of Outsourced Databases with Signature Aggregation and Chaining (Short Paper/Poster)
ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2005), Nov 2005 PDF
-
Efficient Aggregation of Encrypted Data in Wireless Sensor Networks
International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems (MobiQuitous 2005), Jul 2005 PDF
-
Incorporating a Secure Coprocessor in the Database-as-a-Service Model
International Workshop on Innovative Architecture for Future Generation High Performance Processors and Systems (IWIA 2005), Jan 2005 PDF
-
Signature Bouquets: Immutability for Aggregated/Condensed Signatures
European Symposium On Research in Computer Security (ESORICS 2004), Sep 2004 PDF
-
A Privacy-Preserving Index for Range Queries
International Conference on Very Large Databases (VLDB 2004), Aug 2004 PDF
-
A Framework for Efficient Storage Security in RDBMS
International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT 2004), Mar 2004 PDF
-
Authentication and Integrity in Outsourced Databases
Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS 2004), Feb 2004 PDF
-
Efficient Execution of Aggregation Queries over Encrypted Relational Databases
Database Systems for Advanced Applications (DASFAA 2004), Mar 2004
-
Executing SQL over Encrypted Data in the Database-Service-Provider Model
ACM SIGMOD Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD 2002), June 2002 PDF
-
Providing Database as a Service
IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE 2002), Feb 2002 PDF
-
Querying Encrypted XML Documents
UCI Technical Report
-
Aggregation Queries in the
Database-As-a-Service Model
| Presentations |
-
Privacy and Integrity in Outsourced Databases
PDF
Distinguished invited talk at CERIAS, Purdue University, April 2004 -
A Framework for Efficient Storage Security in RDBMS
PDF
Conference presentation at EDBT 2004 -
Authentication and Integrity in Outsourced Databases
PDF
Conference presentation at NDSS 2004